1st Level User Helpdesk
Content
- Definition 1st Level Support
- 1st level support delimitation
- Tasks 1st Level Support
- KPI’s 1st Level Support
- Goals 1st Level Support
- Query customer satisfaction
- Dealing with customer requirements outside the
defined first level support spectrum - Eskalation an den 2nd Level Support
- Dedicated teams and shared teams
- Structure 1st level support


1. Definition 1st Level Support
The provision of 1st level support is based on the ITIL standard (= predefined standards for the provision of IT services):
“The Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL) is a collection of predefined processes, functions and roles typically found in any IT infrastructure of medium and large enterprises.”
IT service management is divided into several categories, including first level support. For first level support, there is ISO certification 20000, an internationally recognized standard on IT Service Management (ITSM) for enterprises. The 1st level support includes remote services only. Pure service delivery and problem resolution does not include on-site visits to customers. On-site control of the employees (internal IT team of the customer) is possible.
2. 1st level support delimitation
1st Level Support is the provision of a service team for a first response point for the user from the IT environment. This can be:
- Hotline (telephone number for the customer)
- Chat (chat function for the customer)
- E-mail system (tickets)
1st level support serves to provide initial assistance to the customer. This is done by means of ticket opening and is always based on a knowledgebase, i.e. a collection of knowledge about the company/products. For a uniform solution of customer inquiries, the 1st level employees refer to the knowledgebase, which contains a question catalog. By means of the knowledgebase, the complexity of the request is classified. For simple questions, it is important to provide the customer with immediate support.
3. Tasks 1st level support
1. receiving customer inquiries via phone, chat, email. Classification of requests in:
- Incident Malfunction; A service is disrupted. Example: Malfunction of the e-mail service.
- Service request example: forgotten password, access to folder/program functionalities.
- Change Request Change request; desire to change the characteristics of a particular product feature. Example: Adobe Reader in use, wish to switch to PDF-XChange Viewer.
2. assistance Within the scope of 1st level support, the following areas apply:
Problems with:
- Hardware (defective notebooks, error messages )
- Periphery
- Operating system
- Microsoft Office
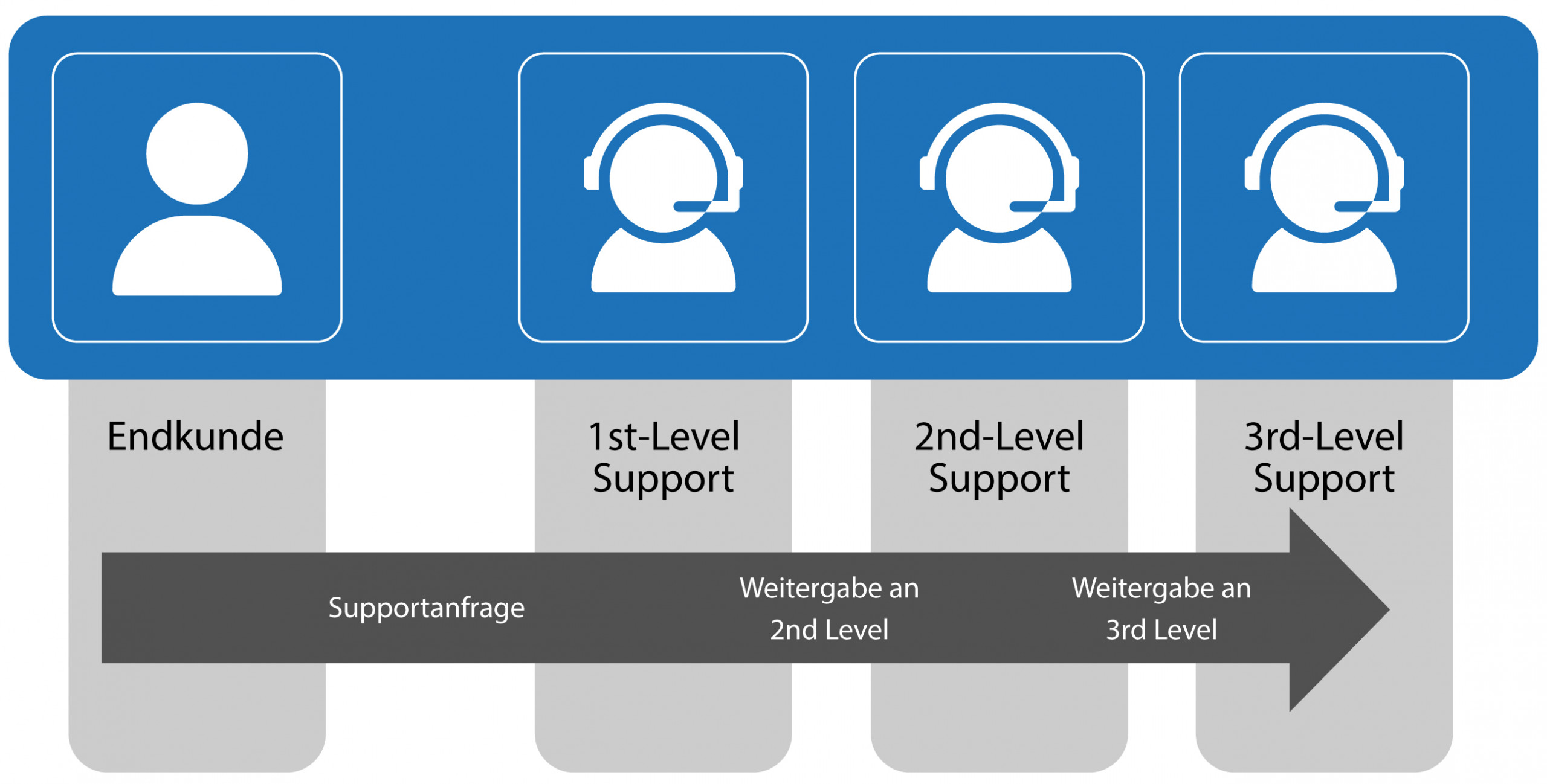
3. in case of complex solution needs, forwarding of tickets to 2nd level support, customer satisfaction queries or support of user applications outside the Windows level. This requires individual coordination with the customer.
4. KPIs 1st Level Support
The time for problem solving within the 1st level support is on average 30 minutes up to a maximum of one hour. If the ticket could not be solved within this time, the ticket is forwarded to 2nd level support. Phone pickup time and chat response time < 20 seconds (this refers to the time from the first ring until a support agent picks up the phone).
5. Goals 1st level support
- User satisfaction: satisfaction rate 90% >
- Ensure rapid accessibility; ideally, accessibility at extended hours.
- Ensuring a quick phone pickup time as well as a quick chat response.
- maximum service quality and high quality customer support.
6. Query customer satisfaction
After the 1st level service, customer satisfaction is queried with the user via e-mail or telephone. The evaluation on the part of the customers is carried out on the basis of the school grading system:
very good (1), good (2), satisfactory (3), sufficient (4), poor (5), insufficient (6)
7. Handling customer requirements outside the defined 1st level support spectrum
If requests reach 1st level support that cannot be classified in the defined areas of hardware, peripherals, operating system and Microsoft Office, the scope of support must be clarified with the customer.
- Example: Customer requests 1st level support for an application that only the customer is using (creation of a new user outside the Windows level
Simple topics can be included in the 1st level portfolio. This requires the customer to provide a knowledge base with maintained entries to ensure homogeneous support. This special knowledge base is not a service of the 1st level support, but has to be provided by the customer. Furthermore, this is based on individual pricing and coordination with the customer.
8. Escalation at 2nd level Support
If a ticket cannot be solved within the 1st level support, the 1st level support will escalate to the corresponding 2nd level support (2nd level support is for: Business Applications, Infrastructure, Network Operations etc.).
9. Dedicated teams and shared teams
Depending on the size of the company being served, the 1st level support help desk may be a dedicated team, i.e. a team that works predominantly for a defined customer and devotes very few resources to other customers. This applies to companies with 1,000 or more workplaces. Shared teams are used for smaller customers ( < 1000 employees), with one team looking after five to six customers.
10. Structure 1st level support
The 1st level support is managed by a service delivery manager, who ensures the service quality (= fast accessibility, fast pickup time, good rate of customer satisfaction surveys as well as their execution, fast problem solving). He also prepares the work plans of the 1st level support team.